Understanding Skin Cancer: Types, Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
Contents
- 1 Understanding Skin Cancer: Types, Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
- 1.1 Introduction
- 1.2 Skin Cancer Types
- 1.3 read more posts
- 1.4 Reasons and Danger Elements
- 1.5 read more posts
- 1.6 Signs and Recognition
- 1.7 read more posts
- 1.8 Diagnosis of Skin Cancer
- 1.9 Assessment and Management
- 1.10 read more posts
- 1.11 Avoidance
- 1.12 In summary
- 1.13 read more posts
- 1.14 FAQs with answers about Skin Cancer:
- 1.15 read more posts
Read DISCLAIMER
Recognize the many forms, causes, signs, and treatments of skin cancer. Discover how to properly manage this illness by learning about early detection symptoms, preventive strategies, and essential insights.
Introduction
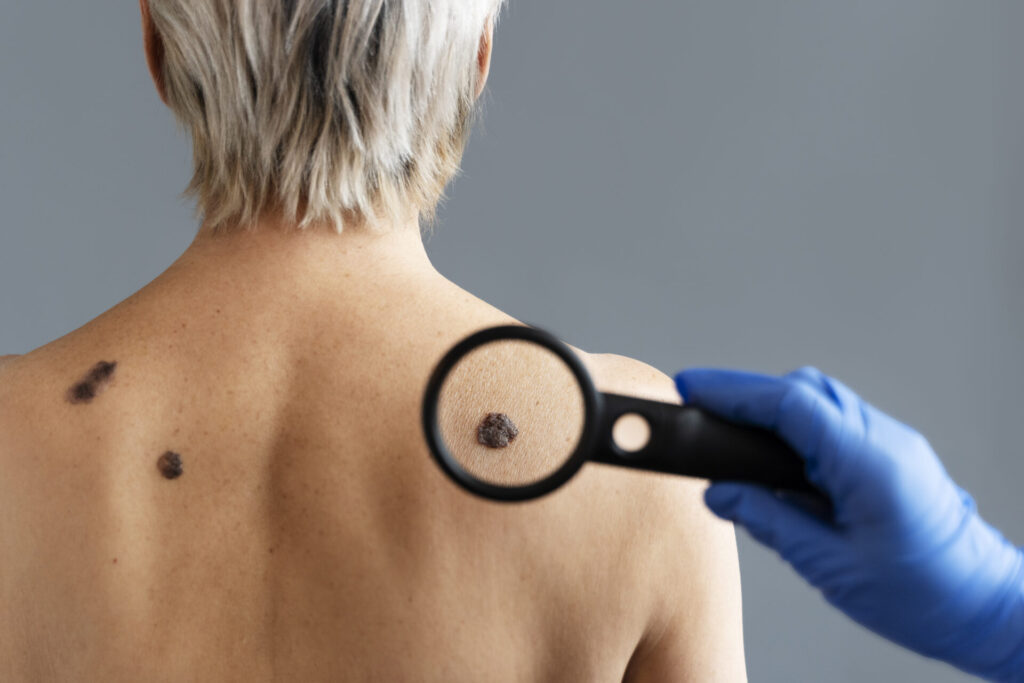
The abnormal development of skin cells is a characteristic of skin cancer. Exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun or artificial sources, such as tanning beds, is the main cause of it. Skin cancer comes in several forms, each with unique traits and methods of treatment.
Skin Cancer Types
1. Basal Cell Carcinoma (BCC): The most prevalent kind, usually manifesting as a pinkish patch of skin or a flesh-colored, pearl-like lump.
2. Squamous Cell Carcinoma (SCC): Usually manifests as a flat sore with a scaly crust or as a solid, red lump. If treatment is not received, it may progress to deeper layers and spread to other locations.
3. Melanoma: The most serious type of the disease, while being less prevalent. It commonly appears on the skin as a new black patch or mole, frequently with erratic boundaries or color changes.
4. Merkel Cell Carcinoma: Less common than the others, this cancer shows up as hard, glossy nodules that might be blue, pink, or red in color.
read more posts
Reasons and Danger Elements
The majority of skin malignancies are primarily caused by excessive UV radiation exposure. Other risk variables consist of:
– Fair Skin: Skin types with a lower melanin content offer poorer defense against UV rays.
– Sun Exposure: Extended periods of time spent in the sun without protection raise the risk.
– Tanning Beds: The risk of skin cancer can be greatly increased by the artificial UV radiation from tanning beds.
– Personal or Family History: People who have a family history of skin cancer are at an increased risk.
– Weakened Immune System: Immune system-suppressive diseases or drugs might make a person more susceptible.
read more posts
Signs and Recognition
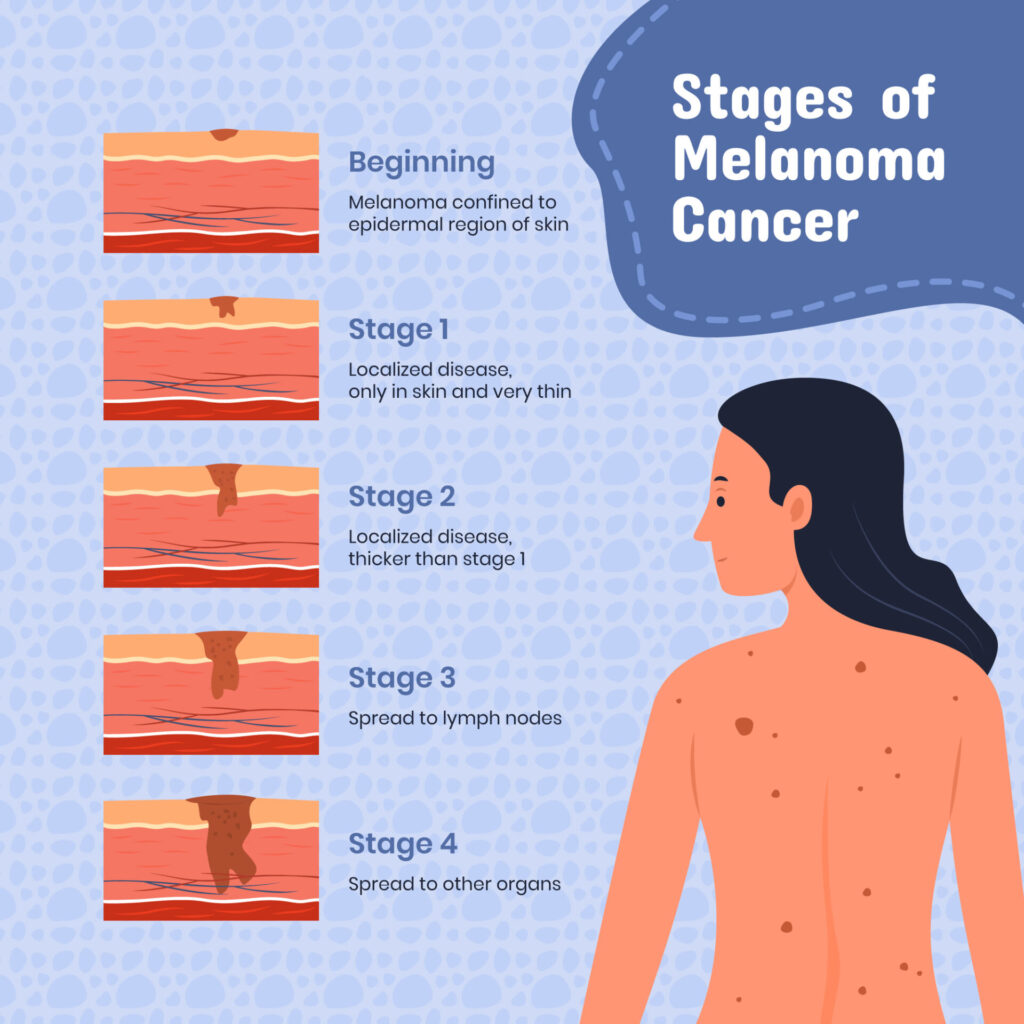
Depending on the kind, skin cancer symptoms might change. Be cautious of:
Asymmetrical form, uneven borders, variations in color or size are examples of modifications in moles or spots.
– New Growth or Sore: A newly formed area or sore that does not go away in a fair amount of time.
– Itching, Pain, or Bleeding: Any uncharacteristic feelings or bleeding from an injury on the skin.
read more posts
Diagnosis of Skin Cancer
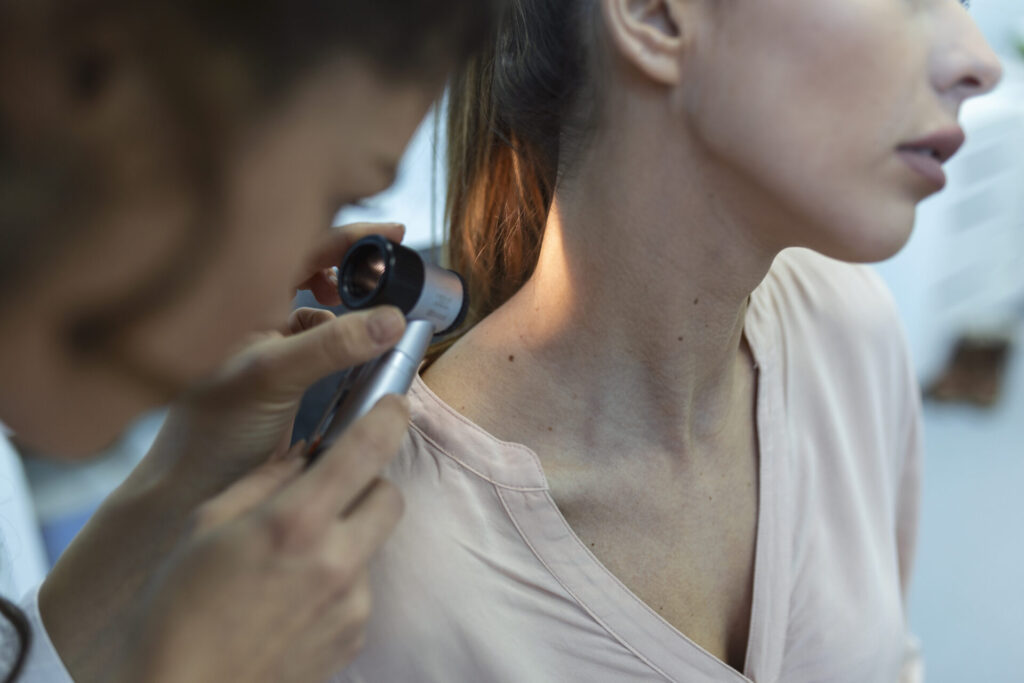

A thorough examination performed by a dermatologist or other healthcare provider with expertise in skin diseases is necessary to diagnose skin cancer. Usually, the procedure entails:
– Visual Examination: The physician looks closely at any unusual growths, lesions, or moles when examining the patient’s skin.
– Dermoscopy: In this procedure, a dermatoscope—a device that enlarges and illuminates the skin—is used to examine skin lesions in more detail.
– Biopsy: Should any regions be found to be questionable, one may do a biopsy. A little sample of the aberrant skin tissue is taken during a biopsy, and it is submitted to a lab for examination. This aids in determining the kind and stage of cancer, as well as if the cells are malignant.
– Extra Tests: To ascertain whether the cancer has progressed outside of the skin, extra tests, such as imaging scans (such as MRI or CT scans), may occasionally be needed.
It’s also advised to regularly examine yourself in order to track any changes in skin lesions or moles. A healthcare provider should inspect any new, changing, or unusual growths right away for a more thorough assessment and diagnosis. Treatment results for skin cancer are markedly improved by early identification achieved through routine skin examinations.
Assessment and Management
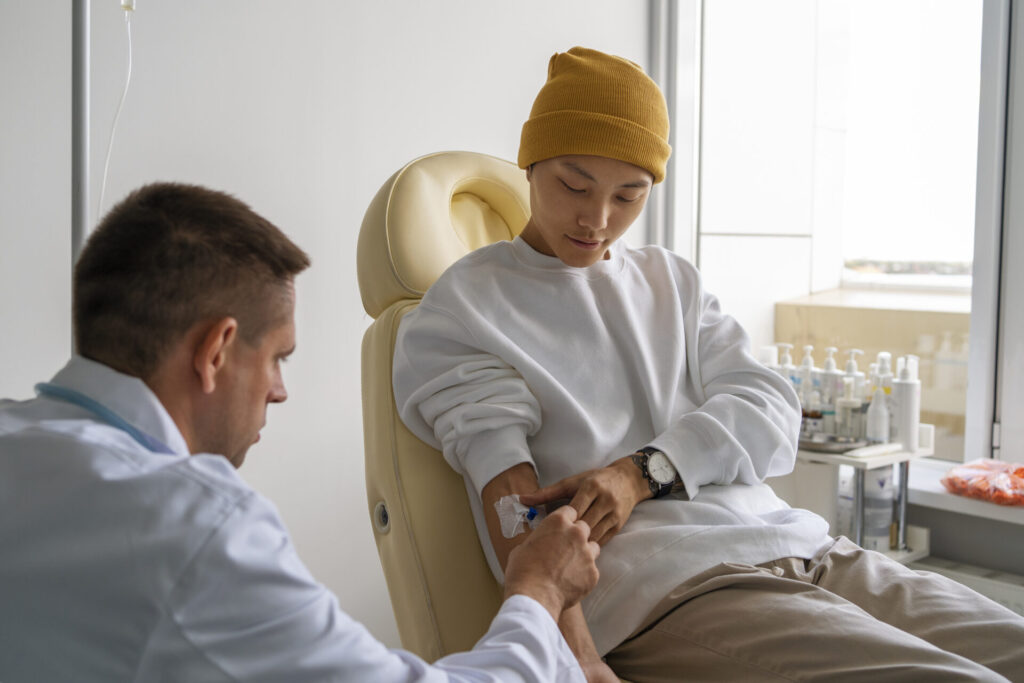
A dermatologist will do a thorough examination and may recommend a biopsy to examine any abnormal skin cells in order to make a diagnosis.
How a skin cancer is treated depends on its form and stage.
– Surgery: To remove tumors or malignant growths.
– Radiation therapy: focused radiation used to kill cancerous cells.
– Chemotherapy: Drugs that either eradicate or inhibit the development of cancer cells.
– Targeted treatment often known as immunotherapy, aims to target certain cancer cells while enhancing the immune system.
read more posts
Avoidance
– Sun Protection: Look for shade during the hottest parts of the day, wear protective clothes, and use sunscreen with an SPF of at least 18.
– Frequent Skin Checks: Look for any changes or anomalies on your skin on a frequent basis.
– Steer clear of tanning beds: Reduce your exposure to artificial UV light.
– Speak with a Dermatologist: Frequent exams can aid in the early detection and treatment of skin cancer.
In summary
A complex disease, sun exposure, genetic predispositions, and other risk factors can all contribute to skin cancer. For early identification, it is essential to comprehend the several varieties of cancer, including Merkel cell carcinoma, melanoma, squamous cell carcinoma, and basal cell carcinoma, as well as its origins and symptoms. Prevention requires vigilance, routine skin exams, and sun protection. The prognosis is greatly impacted by an early diagnosis and suitable treatment methods, such as radiation, immunotherapy, or surgery. Skin cancer’s detrimental effects on people’s health and well-being can be significantly reduced by raising awareness, taking preventative action, and practicing medical vigilance.
In case you see any unusual alterations in your skin, it is advisable to consult a medical expert right once.
read more posts
FAQs with answers about Skin Cancer:
What Is Skin Cancer?
Skin cancer encompasses various abnormal growths of skin cells due to damage from UV radiation or genetic factors. The most prevalent types are Basal Cell Carcinoma, Squamous Cell Carcinoma, Melanoma, and Merkel Cell Carcinoma.
What Does Skin Cancer Look Like?
Skin cancer can manifest in diverse ways depending on its type. Common signs include changes in moles or spots, new growths, sores that don’t heal, and abnormal sensations like itching or pain.
What Cancer Can Cause Itchy Skin?
Squamous Cell Carcinoma and some forms of melanoma may cause itchy skin as a symptom. However, itchiness alone might not always indicate cancer and can be caused by various other skin conditions.
How Do You Get Skin Cancer?
Excessive exposure to UV radiation from the sun or tanning beds is the primary cause. Other risk factors include fair skin, family history, and weakened immune systems.
How to Prevent Skin Cancer?
Prevention involves sun protection, such as using sunscreen, wearing protective clothing, avoiding tanning beds, and regular skin checks for any changes.
What Does Skin Cancer Feel Like?
Skin cancer can cause various sensations like itching, tenderness, or pain. However, not all skin changes or discomfort indicate cancer, but any persistent or unusual sensation should be evaluated by a healthcare professional.
How Do You Know If You Have Skin Cancer?
Changes in moles, new growths, sores that don’t heal, or any abnormal sensations on the skin might indicate skin cancer. Regular self-examinations and professional skin checks are crucial.
What Are the 4 Types of Skin Cancer?
The four main types of skin cancer are Basal Cell Carcinoma, Squamous Cell Carcinoma, Melanoma, and Merkel Cell Carcinoma. Visual references like pictures can help identify suspicious skin changes.
What Are Signs of Skin Cancer?
Signs of skin cancer include changes in the size, shape, or color of moles or spots, new growths, and sores that don’t heal within a reasonable time.
What Is the Most Common Type of Skin Cancer?
Basal Cell Carcinoma is the most common type of skin cancer, typically presenting as flesh-colored bumps or pinkish patches.
How Long Does It Take to Get Skin Cancer from Tanning Beds?
Prolonged exposure to tanning beds can significantly increase the risk of skin cancer, but the exact duration varies based on individual factors and intensity of exposure.
How Common Is Skin Cancer?
Skin cancer is one of the most prevalent forms of cancer globally. Its incidence continues to rise, emphasizing the importance of preventive measures and early detection.
What Does Early Skin Cancer Look Like?
Early skin cancer might resemble changes in moles or spots, irregular borders, color variations, or new growths on the skin.
How Does Skin Cancer Kill You?
If left untreated, skin cancer can spread to other organs, leading to severe complications and potentially fatal outcomes.
How Fast Does Skin Cancer Grow? How Deadly Is Skin Cancer?
The growth rate and lethality of skin cancer vary based on the type and stage. Early detection and appropriate treatment significantly improve outcomes.
How Is Skin Cancer Diagnosed?
Diagnosis involves a thorough examination by a dermatologist and may include a biopsy for further analysis of suspicious skin cells.
What Are the Symptoms of Skin Cancer?
Symptoms include changes in moles, new growths, sores that don’t heal, and unusual sensations on the skin like itching or tenderness.
What Are the Signs of Skin Cancer?
Signs encompass visual changes in moles or spots, new growths, and persistent sores that warrant evaluation by a healthcare professional.
What Is Skin Cancer Called?
Skin cancer refers to the abnormal growth of skin cells due to various causes like UV exposure or genetic predisposition.
How Do I Know If I Have Skin Cancer? How to Identify Skin Cancer?
Self-examinations and professional skin checks can help identify suspicious changes on the skin, facilitating early diagnosis and treatment.
How Bad Is Skin Cancer? What Are Symptoms of Skin Cancer?
Skin cancer, if left untreated, can progress and cause severe complications. Symptoms may include changes in the skin’s appearance, itching, pain, or bleeding.
What Does the Start of Skin Cancer Look Like? What Does Skin Cancer on the Scalp Look Like?
Early signs may include changes in moles, irregular borders, color variations, or new growths. Skin cancer on the scalp may appear as abnormal growths or changes in the skin.
How to Spot Skin Cancer?
Regular self-examinations, awareness of changes in moles or spots, and seeking medical advice for any abnormal skin changes aid in spotting potential skin cancer.
What causes skin cancer?
Excessive UV exposure, genetic factors, and weakened immune systems are common causes.
How do I recognize skin cancer?
Look for changes in moles, new growths, or sores that don’t heal. Any unusual sensations or bleeding from a skin lesion should be checked.
Can skin cancer be prevented?
Yes, using sunscreen, wearing protective clothing, avoiding tanning beds, and regular skin checks are key preventive measures.
What are the treatment options for skin cancer?
Treatments include surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, immunotherapy, or targeted therapy, depending on the type and stage.
read more posts
Your article helped me a lot, is there any more related content? Thanks!
I don’t think the title of your article matches the content lol. Just kidding, mainly because I had some doubts after reading the article.
Thank you for your sharing. I am worried that I lack creative ideas. It is your article that makes me full of hope. Thank you. But, I have a question, can you help me? https://www.binance.com/join?ref=P9L9FQKY
Thanks for sharing. I read many of your blog posts, cool, your blog is very good. https://accounts.binance.com/ro/register-person?ref=HX1JLA6Z
Thanks for sharing. I read many of your blog posts, cool, your blog is very good. https://www.binance.info/ES_la/register?ref=VDVEQ78S
I don’t think the title of your article matches the content lol. Just kidding, mainly because I had some doubts after reading the article.
Your article helped me a lot, is there any more related content? Thanks!