Mpox vs. Smallpox: 7 Key Differences You Need to Understand
Contents
- 1 Mpox vs. Smallpox: 7 Key Differences You Need to Understand
- 1.1 1. Causative Agent
- 1.2 read more posts
- 1.3 2. Historical Impact and Current Status
- 1.4 read more posts
- 1.5 3. Transmission
- 1.6 read more posts
- 1.7 4. Symptoms and Disease Progression
- 1.8 read more posts
- 1.9 5. Mortality Rate
- 1.10 read more posts
- 1.11 6. Vaccine Development and Availability
- 1.12 read more posts
- 1.13 7. Global Public Health Response
- 1.14 read more posts
- 1.15 Conclusion
- 1.16 read more posts
- 1.17 FAQs with Answers
Read DISCLAIMER
Discover the 7 key differences between mpox and smallpox, two Orthopoxviruses with distinct impacts on global health. Learn about their transmission, symptoms, mortality rates, and more in this comprehensive guide for 2024.
Both smallpox and mpox are viral infections that have at various times in history attracted interest from around the world. Despite certain commonalities, such as their classification as orthopoxviruses, they differ significantly in important ways. Comprehending these distinctions is essential for efficacious public health interventions, clinical supervision, and individual consciousness. Here are seven important distinctions between smallpox and mpox that you should be aware of.

1. Causative Agent
– Smallpox : The Orthopoxvirus genus includes the Variola virus, which causes smallpox. There are two main strains of the Variola virus: Variola minor, which is less severe, and Variola major, which is more severe and lethal..
– Mpox: Another member of the Orthopoxvirus genus, the monkeypox virus, is the cause of mpox, also referred to as monkeypox. The monkeypox virus is divided into two clades: the less severe West African clade and the more severe Central African (Congo Basin) clade.
Key Point : While both diseases are caused by Orthopoxviruses, they are different viruses with distinct epidemiological characteristics.
read more posts
2. Historical Impact and Current Status
– Smallpox : Smallpox, especially in its Variola major form, was a deadly disease that caused great suffering. Over centuries, it was the cause of millions of deaths. On the other hand, smallpox was officially declared extinct in 1980 as a result of an effective worldwide immunization drive spearheaded by the World Health Organization (WHO).
– Mpox : Compared to smallpox, mpox has not had the same extensive impact. With occasional outbreaks in other parts of the world, it mainly affects regions in Central and West Africa. In contrast to smallpox, which has been eradicated, mpox remains a public health concern, especially in regions where the virus is prevalent.
Key Point : Smallpox is a historical disease with no current cases, whereas mpox remains an active public health issue in certain regions.
read more posts
3. Transmission
– Smallpox : In intimate, face-to-face contact with an infected individual, respiratory droplets are the main way that smallpox is transmitted. Additionally, it can spread by coming into contact with contaminated clothing or bedding. Particularly when the rash was still in its early stages, the virus was extremely infectious.
– Mpox : Direct contact with an infected human or animal’s body fluids, skin lesions, or respiratory droplets can result in the spread of mpox. Additionally, coming into contact with contaminated materials can spread it. Mumps is less contagious than smallpox and usually spreads through closer, longer contact.
Key Point : Mpox has a lower transmission rate compared to smallpox, with different modes of transmission that often require direct contact with infected individuals or animals.

read more posts
4. Symptoms and Disease Progression
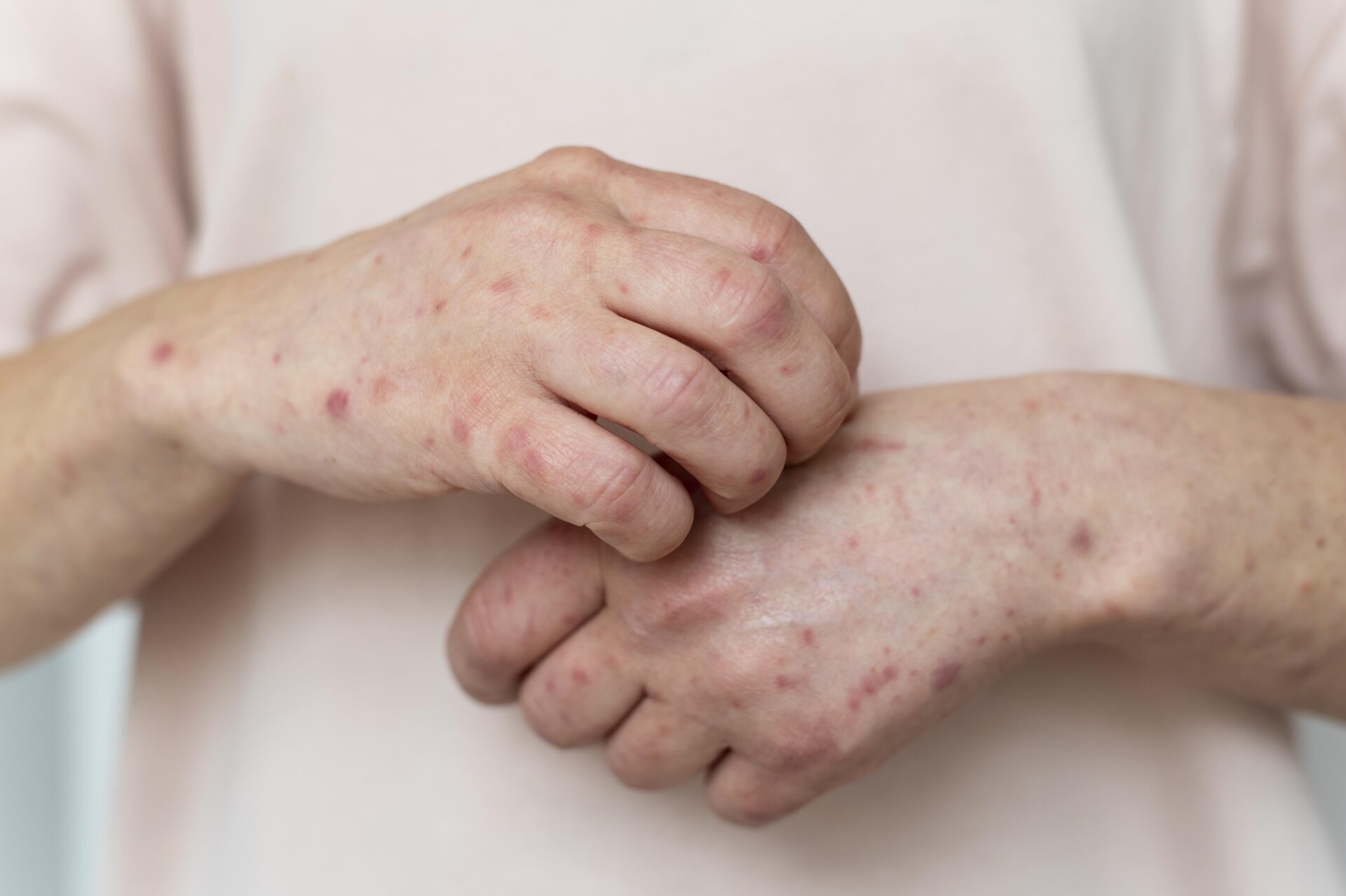
– Smallpox : Smallpox symptoms include high fever, exhaustion, headache, and back discomfort. A rash that starts on the face and spreads to the extremities is the typical smallpox symptom. From macules to papules, vesicles and pustules, and finally scabs, the rash developed. Smallpox progressed predictably and had a more severe course of the illness.
– Mpox : Along with a rash that frequently begins on the face and moves to other parts of the body, such as the palms and soles, mpox symptoms also include fever, headache, muscular aches, and other symptoms. While more confined in nature, smallpox and mpox lesions are comparable. Smallpox rarely exhibits lymphadenopathy, or enlarged lymph nodes, which is a characteristic of mpox.
Key Point : Both diseases cause rashes, but mpox often presents with swollen lymph nodes and a more localized rash, whereas smallpox had a more severe and widespread rash without lymphadenopathy.
read more posts
5. Mortality Rate
– Smallpox : Depending on the strain, smallpox mortality rates differed. Variola major was an extremely deadly disease, with a death rate of roughly 30%. Variola minor usually has a mortality rate of about 1%.
– Mpox : Compared to smallpox, mpox has a substantially lower death rate. The monkeypox virus’s West African clade has a fatality rate of less than 1%, while the Central African clade has a mortality rate of over 10%.
Key Point : Smallpox had a much higher mortality rate than mpox, with the potential to kill a significant proportion of those infected.
read more posts
6. Vaccine Development and Availability
– Smallpox : The first vaccination to be developed successfully was the smallpox vaccine, which was created by Edward Jenner in 1796 using the cowpox virus. The smallpox epidemic was eradicated worldwide in large part thanks to this vaccination. Since smallpox has been eradicated, vaccinations against it are no longer regularly given.
– Mpox : Modified smallpox vaccines, including JYNNEOS (also known as Imvamune or Imvanex), are the basis for mpox vaccines. Currently, those who are more susceptible to contracting mpox, such as healthcare personnel and residents of areas where the disease is endemic, are administered these vaccinations.
Key Point : The development of smallpox vaccines led to the eradication of the disease, while mpox vaccines are adaptations of these vaccines, used primarily for at-risk populations.
read more posts
7. Global Public Health Response
– Smallpox : Throughout history, one of the most effective public health initiatives has been the worldwide response to smallpox. Launched in 1967, the World Health Organization’s Intensified Smallpox Eradication Programme resulted in the last smallpox case occurring naturally in 1977, with the disease being declared eradicated in 1980.
– Mpox : The response to mpox has been more localized, with efforts focused on surveillance, containment, and vaccination in regions where the virus is endemic. International attention to mpox has increased in recent years due to outbreaks outside Africa, prompting a more coordinated global response.
Key Point : Smallpox was eradicated through a concerted global effort, while mpox remains a public health challenge that requires ongoing attention, particularly in endemic regions.
read more posts
Conclusion
Critical distinctions between smallpox and mpox are highlighted in the comparison, with important ramifications for medical therapy, public health, and worldwide awareness. Through an unparalleled worldwide vaccination campaign, smallpox—once one of the deadliest illnesses in human history—was eradicated, demonstrating the strength of teamwork in defeating even the most difficult health threats. On the other hand, mpox continues to pose a chronic threat, especially in areas where the virus is endemic.
Although both diseases are related to the Orthopoxvirus genus, their effects and the approaches needed to treat them are different, as seen by the variations in their modes of transmission, degrees of disease severity, and death rates. Compared to smallpox, which is already eradicated, mpox presents a distinct kind of threat due to its lower death rate and less effective spread. Nonetheless, a strong basis for managing and possibly even eradicating mpox is provided by the availability of vaccinations and the knowledge acquired from the eradication of smallpox.
As global health continues to evolve, understanding these differences is crucial for developing effective public health policies, educating the public, and fostering international cooperation. By learning from the past and applying that knowledge to current and future challenges, we can better protect populations from the threats posed by diseases like mpox, ensuring a healthier and safer world for all.
read more posts
FAQs with Answers
1. What is the primary difference between mpox and smallpox?
Mpox is caused by the Monkeypox virus, while smallpox was caused by the Variola virus. Although both are Orthopoxviruses, they differ in severity, transmission, and global impact.
2. Are mpox and smallpox equally contagious?
No, smallpox was more contagious than mpox, spreading mainly through respiratory droplets. Mpox requires closer, prolonged contact with an infected person or animal.
3. Can mpox be as deadly as smallpox?
No, mpox generally has a lower mortality rate compared to smallpox. The Central African clade of the Monkeypox virus has a mortality rate of around 10%, while smallpox had a mortality rate of about 30% for Variola major.
4. How do the symptoms of mpox and smallpox differ?
Both diseases cause rashes, but mpox often includes swollen lymph nodes (lymphadenopathy), which is not typical in smallpox. Smallpox had a more severe and widespread rash.
5. Is there a vaccine for mpox?
Yes, vaccines like JYNNEOS, originally developed for smallpox, are used to protect against mpox, particularly for at-risk populations.
6. Why was smallpox eradicated, but mpox is not?
Smallpox was eradicated through a global vaccination campaign, whereas mpox continues to exist due to its zoonotic nature and the lack of a similarly coordinated global eradication effort.
7. Can smallpox come back?
Smallpox is considered eradicated, and there are no natural cases. However, concerns remain about potential use as a bioterrorism agent.
8. How does the rash in mpox differ from smallpox?
Mpox rashes often start on the face and spread to other parts of the body, including palms and soles. In contrast, smallpox rashes were more widespread and severe.
9. Where is mpox most commonly found?
Mpox is most commonly found in Central and West Africa, with occasional outbreaks in other regions due to travel or contact with infected animals.
10. What measures are taken to control mpox outbreaks?
Control measures include surveillance, isolation of cases, vaccination of at-risk individuals, and public health education.
11. Can animals spread mpox?
Yes, mpox can be transmitted from animals to humans, particularly through direct contact with infected animals or their bodily fluids.
12. Was there a similar global effort to eradicate mpox as there was for smallpox?
No, the global effort to eradicate smallpox was unique and highly coordinated, while efforts to control mpox are more localized and focused on endemic regions.
13. Is the smallpox vaccine effective against mpox?
Yes, the smallpox vaccine provides some cross-protection against mpox due to the similarity between the viruses.
14. Are there any long-term effects of surviving mpox?
Survivors of mpox may experience scarring from the rash, but long-term effects are generally less severe than those from smallpox, which could cause blindness and other complications.
15. How do public health responses to mpox differ from those to smallpox?
Public health responses to mpox focus on containment, vaccination, and education in endemic regions, while the smallpox response was a global eradication effort.
Read more about Mpox
Mpox in 2024: What Weve Learned and What Lies Ahead
Is Mpox Becoming More Contagious? Understanding the Risks and Trends in 2024
Mpox and Climate Change: A Growing Concern
Long-Term Health Effects of Mpox: What We Know So Far rm-health-effects-of-mpox-what.html
Mpox and Global Health Security: Lessons Learned
Addressing Mpox Stigma and Discrimination: A 2024 Perspective
The Role of Contact Tracing in Mpox Prevention
The quality of your work here is outstanding. The design and writing style are both impressive. There’s a unique flair in your approach, and I’ll definitely return to see what else you have to offer.
Hello there! This post couldn’t be written any better! Reading this post reminds me of my good old room mate! He always kept talking about this. I will forward this post to him. Pretty sure he will have a good read. Thanks for sharing!
Wonderful work! This is the type of info that should be shared around the web. Shame on Google for not positioning this post higher! Come on over and visit my site . Thanks =)
Thanks , I’ve recently been looking for information about this topic for a while and yours is the best I’ve came upon so far. But, what concerning the conclusion? Are you sure about the source?
Good post. I learn something totally new and challenging on websites I stumbleupon on a daily basis.
It will always be interesting to read through articles from other writers and use something
from other sites.
Also visit my web page – nordvpn coupons inspiresensation (t.co)
Thanks for the marvelous posting! I seriously enjoyed reading it, you will be a great author.I will remember to bookmark your blog and will eventually come back later in life. I want to encourage one to continue your great posts, have a nice holiday weekend!
In line with my study, after a the foreclosure home is sold at a sale, it is common to the borrower in order to still have the remaining balance on the mortgage loan. There are many loan companies who make an effort to have all rates and liens paid by the future buyer. Nonetheless, depending on specified programs, regulations, and state legal guidelines there may be a few loans that are not easily solved through the shift of personal loans. Therefore, the responsibility still rests on the customer that has received his or her property foreclosed on. Many thanks sharing your notions on this web site.
Well I really enjoyed reading it. This post provided by you is very practical for correct planning.
Hey there! Do you know if they make any plugins to safeguard against hackers? I’m kinda paranoid about losing everything I’ve worked hard on. Any tips?
F*ckin?remarkable things here. I抦 very glad to see your article. Thanks a lot and i’m looking forward to contact you. Will you please drop me a mail?
What抯 Happening i am new to this, I stumbled upon this I’ve found It absolutely helpful and it has aided me out loads. I hope to contribute & assist other users like its helped me. Great job.
Wow! Thank you! I continuously wanted to write on my website something like that. Can I implement a fragment of your post to my website?
Just wish to say your article is as astonishing. The clarity to your publish is just great and i can assume you are knowledgeable in this subject. Well together with your permission allow me to snatch your feed to stay updated with coming near near post. Thank you one million and please continue the enjoyable work.
Can I just say what a aid to find someone who really knows what theyre talking about on the internet. You undoubtedly know learn how to carry a problem to mild and make it important. Extra individuals need to learn this and perceive this side of the story. I cant imagine youre not more popular since you undoubtedly have the gift.
Yesterday, while I was at work, my cousin stole my apple ipad and tested to see if it can survive a 25 foot drop, just so she can be a youtube sensation. My iPad is now broken and she has 83 views. I know this is totally off topic but I had to share it with someone!
Howdy! I simply would like to give a huge thumbs up for the nice info you may have right here on this post. I will be coming back to your blog for extra soon.
Good web site! I really love how it is simple on my eyes and the data are well written. I’m wondering how I could be notified whenever a new post has been made. I’ve subscribed to your feed which must do the trick! Have a great day!
My partner and I stumbled over here by a different page and thought I should check things out. I like what I see so now i’m following you. Look forward to looking over your web page yet again.
Its like you read my thoughts! You appear to know a lot approximately this, such as you wrote the e-book in it or something. I believe that you could do with some to power the message home a little bit, but instead of that, that is excellent blog. An excellent read. I’ll certainly be back.
Hi, i think that i saw you visited my web site so i came to 搟go back the prefer?I’m attempting to find things to improve my site!I assume its adequate to make use of some of your concepts!!
I was curious if you ever thought of changing the structure of your website? Its very well written; I love what youve got to say. But maybe you could a little more in the way of content so people could connect with it better. Youve got an awful lot of text for only having 1 or two pictures. Maybe you could space it out better?
hello!,I like your writing very much! proportion we communicate extra approximately your article on AOL? I need an expert in this house to solve my problem. Maybe that is you! Looking forward to see you.
You can certainly see your expertise in the work you write. The world hopes for more passionate writers like you who aren’t afraid to say how they believe. Always follow your heart.
One thing I’d really like to say is the fact that before purchasing more computer system memory, check out the machine in which it could well be installed. If your machine is definitely running Windows XP, for instance, the actual memory threshold is 3.25GB. Using over this would merely constitute a new waste. Be sure that one’s mother board can handle your upgrade volume, as well. Good blog post.
certainly like your website but you have to check the spelling on quite a few of your posts. Several of them are rife with spelling problems and I find it very bothersome to tell the truth nevertheless I will definitely come back again.
Normally I do not read post on blogs, but I wish to say that this write-up very forced me to try and do so! Your writing style has been amazed me. Thanks, quite nice post.
Attractive component of content. I just stumbled upon your website and in accession capital to say that I acquire in fact enjoyed account your blog posts. Anyway I抣l be subscribing in your augment and even I achievement you get admission to constantly rapidly.
When I originally commented I clicked the “Notify me when new comments are added” checkbox and now each time a comment is added I get three emails with the same comment. Is there any way you can remove people from that service? Thanks a lot!
Your articles are very helpful to me. May I request more information? http://www.ifashionstyles.com
Thank you for another informative blog. The place else may I get that type of info written in such a perfect means? I have a mission that I’m just now working on, and I have been on the glance out for such information.
After study a couple of of the weblog posts in your web site now, and I truly like your approach of blogging. I bookmarked it to my bookmark website listing and will be checking back soon. Pls take a look at my web site as properly and let me know what you think.
Wonderful beat ! I wish to apprentice while you amend your site, how could i subscribe for a blog web site? The account helped me a acceptable deal. I had been tiny bit acquainted of this your broadcast provided bright clear idea
I抦 no longer sure where you’re getting your info, however great topic. I must spend a while studying more or figuring out more. Thank you for magnificent information I used to be on the lookout for this information for my mission.
Thank you for providing me with these article examples. May I ask you a question? http://www.ifashionstyles.com
Pretty great post. I simply stumbled upon your weblog and wished to mention that I have really loved surfing around your weblog posts. In any case I will be subscribing on your feed and I am hoping you write once more soon!
Your article helped me a lot, is there any more related content? Thanks!
You can certainly see your expertise in the work you write. The world hopes for more passionate writers like you who are not afraid to say how they believe. Always go after your heart.
Hey there! I could have sworn I’ve been to this site before but after browsing through some of the post I realized it’s new to me. Anyhow, I’m definitely glad I found it and I’ll be book-marking and checking back frequently!
whoah this blog is fantastic i like reading your posts. Keep up the great paintings! You recognize, lots of persons are looking around for this info, you can aid them greatly.
Thanks for your posting. One other thing is when you are promoting your property all on your own, one of the challenges you need to be aware about upfront is how to deal with property inspection accounts. As a FSBO vendor, the key towards successfully switching your property in addition to saving money on real estate agent income is understanding. The more you know, the more stable your home sales effort will probably be. One area where by this is particularly important is home inspections.
I do enjoy the way you have framed this problem and it does supply me some fodder for thought. On the other hand, through everything that I have personally seen, I simply just wish as the feed-back pack on that people today remain on issue and don’t start on a soap box regarding the news du jour. Yet, thank you for this outstanding point and even though I do not necessarily concur with this in totality, I value the perspective.
Have you ever considered about adding a little bit more than just your articles? I mean, what you say is important and all. However think about if you added some great graphics or videos to give your posts more, “pop”! Your content is excellent but with images and clips, this blog could certainly be one of the very best in its field. Fantastic blog!
Excellent site. Lots of useful info here. I am sending it to some pals ans also sharing in delicious. And of course, thank you for your effort!
Please tell me more about this. May I ask you a question? http://www.ifashionstyles.com
Wow, marvelous blog layout! How long have you been blogging for? you made blogging look easy. The overall look of your website is excellent, let alone the content!
Hey! Do you know if they make any plugins to help with SEO? I’m trying to get my blog to rank for some targeted keywords but I’m not seeing very good gains. If you know of any please share. Kudos!
I’m extremely impressed with your writing abilities as smartly as with the structure in your weblog. Is this a paid subject matter or did you customize it yourself? Anyway keep up the excellent high quality writing, it抯 uncommon to look a great blog like this one these days..
you have a fantastic blog right here! would you prefer to make some invite posts on my weblog?
May I request that you elaborate on that? http://www.hairstylesvip.com Your posts have been extremely helpful to me. Thank you!
I’d like to find out more? I’d love to find out more details. http://www.kayswell.com
You helped me a lot by posting this article and I love what I’m learning. http://www.kayswell.com
I really appreciate your help http://www.kayswell.com
Please provide me with more details on the topic http://www.ifashionstyles.com
Please tell me more about your excellent articles http://www.kayswell.com
I enjoyed reading your piece and it provided me with a lot of value. http://www.kayswell.com
May I request that you elaborate on that? http://www.hairstylesvip.com Your posts have been extremely helpful to me. Thank you!
Thank you for your articles. I find them very helpful. Could you help me with something? http://www.hairstylesvip.com
Thanks for posting. I really enjoyed reading it, especially because it addressed my problem. http://www.ifashionstyles.com It helped me a lot and I hope it will help others too.
You’ve been great to me. Thank you! http://www.goodartdesign.com
Thank you for providing me with these article examples. May I ask you a question? http://www.kayswell.com
Please provide me with more details on the topic http://www.ifashionstyles.com
Thanks for sharing. I read many of your blog posts, cool, your blog is very good.
What’s up, the whole thing is going fine here and ofcourse every one is sharing information,
that’s actually excellent, keep up writing.
Your tone is very approachable and human. It didn’t feel like a lecture but rather guidance from a knowledgeable friend.
This article is a perfect balance of education and motivation. It not only informed me but also encouraged me to take small steps in the right direction.
What I loved most is how your writing balances facts with simplicity. Even someone new to the topic can grasp the concepts easily without feeling overwhelmed.
I have to say, this article felt like more than just reading—it was an experience. The information, the flow, the tone, and the subtle encouragement throughout all worked together to leave a lasting impression. It’s clear you put your heart, mind, and effort into this, and it shows beautifully.Genial experiencia en Uhmegle español.
Unlike some other platforms, Uhmegle video doesn’t freeze or lag during calls. That makes the conversation flow much better.
I recommend checking out Uhmegle for video calls.
I don’t think the title of your article matches the content lol. Just kidding, mainly because I had some doubts after reading the article.
Your point of view caught my eye and was very interesting. Thanks. I have a question for you.
Thanks for posting! I usually recommend https://www.omegletv.tv/
Your point of view caught my eye and was very interesting. Thanks. I have a question for you.
I don’t think the title of your article matches the content lol. Just kidding, mainly because I had some doubts after reading the article.
Your article helped me a lot, is there any more related content? Thanks!
Thank you for your sharing. I am worried that I lack creative ideas. It is your article that makes me full of hope. Thank you. But, I have a question, can you help me?
Thank you for your sharing. I am worried that I lack creative ideas. It is your article that makes me full of hope. Thank you. But, I have a question, can you help me?
… [Trackback]
[…] Read More here: balancedhealthjourney.com/mpox-vs-smallpox-7-key-differences-you-need-to-understand/ […]
I don’t think the title of your article matches the content lol. Just kidding, mainly because I had some doubts after reading the article. https://accounts.binance.com/sv/register-person?ref=GQ1JXNRE